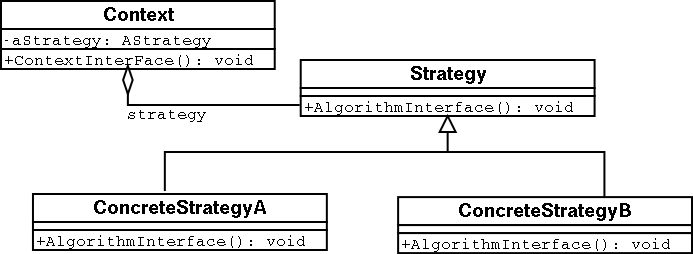
- The
URLclass uses the strategy design pattern [3]. (GoF:315). It separates the algorithm from the host class, thereby allowing multiple algorithms. - The URL class uses it to transparently support multiple protocols:
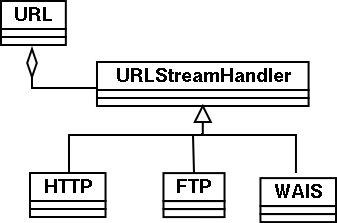

URL class uses the strategy
design pattern [3]. (GoF:315). It separates the algorithm from
the host class, thereby allowing multiple algorithms.
try { //Open it with a url URL u = new URL("http://jmvidal.cse.sc.edu"); //or with separate parts URL u2 = new URL("http", "jmvidal.cse.sc.edu", "/"); InputStream in = URL.openStream(); //strips headers int c; while ((c = in.read()) ~= -1) { write(c); } URLConnection uc = url.openConnection(); //keeps headers InputStream in2 = uc.getInputStream(); //Get content and try to convert it it apporpiate object // using the provided MIME information. Object o = url.getContent(); //Eliminates bad characters, like spaces URLEncoded.encode("A b"); //A+b //Simple way to fetch a document: URLClient client = new URLClient(); String yahoo = client.getDocumentAt("http://www.yahoo.com"); System.out.println(yahoo); } catch (MalformedURL Exception e){ } catch (IOException e) e) { }
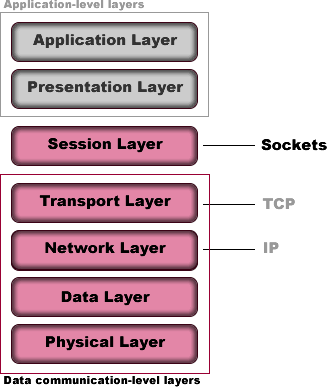
| Client | Server | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
import java.net.*; import java.io.*; public class LowPortScanner { public static void main(String[] args) { //A hostname String host = "localhost"; if (args.length > 0) { host = args[0]; } for (int port = 1; port < 1024; port++) { try { //Open a socket. Socket s = new Socket(host, port); System.out.println("There is a server on port " + port + " of " + host); } catch (UnknownHostException e) { System.err.println(e); break; } catch (IOException e) { // must not be a server on this port } } // end for } // end main } // end PortScanner
socket.getInetAddress() setPort()getLocalPort() returns the number of the local portgetInputStream() returns an InputStream you can read() from.getOutputStream()close(), shutdownInput(), shutdownOutput()ServerSocket on some port.accept.getInputStream() or
getOutputStream() to get a stream.close().import java.net.*; import java.io.*; import java.util.Date; public class DaytimeServer { //You need to be running as root to use ports < 1024. public final static int DEFAULT_PORT = 13; public static void main(String[] args) { int port = DEFAULT_PORT; if (args.length > 0) { try { port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); if (port < 0 || port >= 65536) { System.out.println("Port must between 0 and 65535"); return; } } catch (NumberFormatException e) { // use default port } } try { //Create a server socket. ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(port); //When someone connects we will have a socket. Socket connection = null; while (true) { try { connection = server.accept(); //blocks until someone connects. OutputStreamWriter out = new OutputStreamWriter(connection.getOutputStream()); Date now = new Date(); out.write(now.toString() +"\r\n"); //write to it. out.flush(); //make sure we do write it all. connection.close(); } catch (IOException e) {} finally { try { if (connection != null) connection.close(); } catch (IOException e) {} } } // end while } // end try catch (IOException e) { System.err.println(e); } // end catch } // end main } // end DaytimeServer
import java.net.*; import java.io.*; import java.security.*; import javax.net.ssl.*; public class HTTPSClient { public static void main(String[] args) { if (args.length == 0) { System.out.println("Usage: java HTTPSClient host"); return; } int port = 443; // default https port String host = args[0]; try { //Uses the factory design pattern. SSLSocketFactory factory = (SSLSocketFactory) SSLSocketFactory.getDefault(); SSLSocket socket = (SSLSocket) factory.createSocket(host, port); // enable all the suites String[] supported = socket.getSupportedCipherSuites(); socket.setEnabledCipherSuites(supported); Writer out = new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()); // https requires the full URL in the GET line out.write("GET http://" + host + "/ HTTP/1.1\r\n"); out.write("\r\n"); out.flush(); // read response BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); int c; while ((c = in.read()) != -1) { System.out.write(c); } out.close(); in.close(); socket.close(); } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println(e); } } }
import java.net.*; public class DatagramExample { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "This is a test."; byte[] data = s.getBytes(); try { InetAddress ia = InetAddress.getByName("www.sc.edu"); int port = 7; //create a packet. DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(data, data.length, ia, port); System.out.println("This packet is addressed to " + dp.getAddress() + " on port " + dp.getPort()); System.out.println("There are " + dp.getLength() + " bytes of data in the packet"); System.out.println( new String(dp.getData(), dp.getOffset(), dp.getLength())); //create a socket. DatagramSocket theSocket = new DatagramSocket(); //send it. theSocket.send(dp); } catch (UnknownHostException e) { System.err.println(e); } } }
connect(host, port, ..).import java.net.*; import java.io.*; public abstract class UDPServer extends Thread { private int bufferSize; // in bytes protected DatagramSocket ds; public UDPServer(int port, int bufferSize) throws SocketException { this.bufferSize = bufferSize; ds = new DatagramSocket(port); } public UDPServer(int port) throws SocketException { //8192 is buffersize this(port, 8192); } public void run() { byte[] buffer = new byte[bufferSize]; while (true) { DatagramPacket incoming = new DatagramPacket(buffer, buffer.length); try { ds.receive(incoming); //blocks for packet. respond(incoming); } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println(e); } } // end while } // end run public abstract void respond(DatagramPacket request); //implement this to answer back. }
This talk available at http://jmvidal.cse.sc.edu/talks/javasockets/
Copyright © 2009 José M. Vidal
.
All rights reserved.
28 May 2002, 08:35AM